How do I get the nbn™
The nbn™ is being rolled out Australia wide and by 2020 11.7 million addresses will be ready to connect.
So, how do I get the nbn™ ?
You can check your nbn™ readiness and what technology will be used with the following rollout link. Once your location is ready you should receive a confirmation letter and you can then choose your ISP and pick your plan.
It pays to shop around, cheap is not always the best option. The ISP, depending on the technology used, may send additional hardware to you for a self install before they will activate their connection over the nbn™ installation.
The Digital Consulting Group has a range of nbn™ plans and other broadband internet options - fibre and 4G targeted at the business sector. All plans are designed to provide voice quality connections to support business phone systems.
For most homes and businesses, transitioning to the NBN means moving from an existing ADSL, cable modem or satellite service to one of the services offered by the NBN. The NBN provides Internet services to different locations using a variety of different technologies, referred to as the Multi Technology MIX (MTM), which are:
FTTP (Fibre to the Premises)
FTTN (Fibre to the Node)
FTTB (Fibre to the Building)
FTTC (Fibre to the Curb)
HFC (Hybrid Fibre Co-Axial)
Fixed Wireless
Satellite (Sky Muster)
FTTP (Fibre to the Premises)
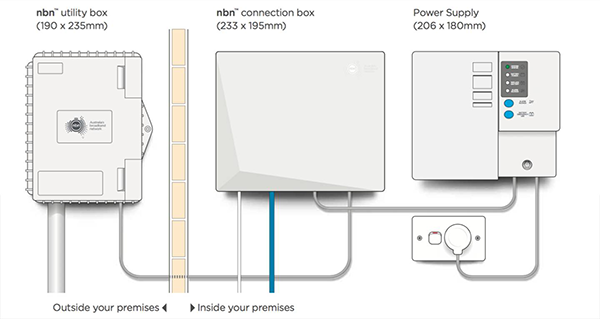
FTTP (Fibre to the Premises) involves running optic fibre directly to inside the premises. nbn™ will install a utility box outside the premises and an nbn™ connection box inside the premises. The nbn™ connection box has a built-in patch panel and a telephone outlet. The Digital Consulting Group can bundle a router with your service but any router with an Ethernet WAN port can be connected to the nbn™ connection box.
FTTN (Fibre to the Node)
FTTN (Fibre to the Node) is the most common nbn™ type and utilises existing copper cabling from a DSLAM (node) in the area to the premises. The fibre node would usually be a cabinet in the street somewhere within a kilometer or so of the premises, with copper cabling running from that right up to a modem/router installed inside the premises to provide the Internet and telephone services. The technology used for this “last mile” of copper is called VDSL (Very high speed digital subscriber line), which is similar to ADSL (Asymmetric digital subscriber line) but faster over shorter distances. VDSL requires a special modem to support it. The Digital Consulting Group can include a suitable router with your service.
FTTB (Fibre to the Building)
FTTB (Fibre to the Building) sometimes called Fibre to the Basement, is almost the same as FTTN but in this case the fibre node is placed in an apartment block’s communications room, which is often found in the basement. Again VDSL is employed to send the data to the individual apartments from the communications room, and the equipment installed inside the premises is the same as found in FTTN connections. The Digital Consulting Group can include a suitable router with your service.
FTTC (Fibre to the Curb)
FTTC (Fibre to the Curb) also utilises copper cabling to the premises but the DSLAM in this case is called a DPU (Distribution Point Unit) and is located a much shorter distance away in a pit in the street just outside the premises. The DPU requires power which comes from the customer premises using the same copper cable that the data is transmitted over. The technology used to send data at high speed from the DPU to the nbn™ connection box inside the premises is another type of DSL technology called G.Fast. The nbn™ connection box in this case is a special type of modem which can support the G.Fast connection as well as the technology to power the DPU in the street. The Digital Consulting Group can include a suitable router with your service.
HFC (Hybrid Fibre Co-Axial)
HFC (Hybrid Fibre Co-Axial) is similar to FTTN but in this case the “last mile” is the same co-axial cable used by the Cable TV network. The nbn™ connection box is a special type of modem, similar to a cable modem, which will be installed in the premises by an approved nbn™ installer. The ISP will then often provide a router/gateway to connect to the NBN Connection box to provide the Internet and telephone services. The Digital Consulting Group can include a suitable router with your service.
Fixed wireless and Satellite (Skymuster)
Fixed wireless and Satellite nbn™ connections are used in areas where it is uneconomical to install optic fibre. Satellite services are used in remote areas where it is not possible to provide fixed cabling or provide the Fixed Wireless solution. For these types of connections, an antenna or satellite dish will be installed outside the premises and connected to an nbn™ connection box/modem inside. A router/gateway will then be connected to the nbn™ connection box to provide the Internet and telephone services.
Transitioning Phone Services to the NBN
Many installations have PSTN phone systems which are connected to copper cabling. As part of the nbn™ rollout, the copper cabling to the exchanges are removed and replaced by an optic fibre to the DSLAM or premises. As a result, all phone services are moved to VoIP (Voice over IP) which requires a router to provide phone services. The Digital Consulting Group can include a suitable router supply a router which provides connectivity to the nbn™ as well as the VoIP service retaining the existing phone numbers.
For most domestic users, the solution provided by the service provider will be adequate. However, for businesses this solution will not be suitable, especially if you need advanced business features such as VPN, firewall security, user management, Quality of Service etc. This may require replacing your basic router with a business grade router.
If you want to retain your existing phone number(s), which will be important for many businesses, the Digital Consulting Group can manage this process and provide VoIP services as well.
Below is the current list of nbn® service classes and their meanings (updated 22/04/2020). Please read below for the meanings of some of these key terms.
| Service Class | Service Class Definition |
| Service Class 0 | The site is planned to be serviced by fibre |
| Service Class 1 | The site is serviceable by fibre, with no PCD or NTD in place |
| Service Class 2 | The site is serviceable by fibre, PCD is installed, no NTD in place |
| Service Class 3 | The site is serviceable by fibre, PCD and NTD are installed |
| Service Class 4 | The site is planned to be serviceable by fixed wireless NBN |
| Service Class 5 | The site is serviceable by fixed wireless NBN, no antenna or NTD in place |
| Service Class 6 | The site is serviceable by fixed wireless NBN, antenna and NTD are installed |
| Service Class 7 | The site is planned to be serviceable by satellite |
| Service Class 8 | The site is serviced by satellite (dish/NTD not installed) |
| Service Class 9 | The site is services by satellite (dish/HTD already installed) |
| Service Class 10 | Site is planned to be serviceable by copper (FTTN or FTTB) |
| Service Class 11 | Site is serviceable by copper, copper lead-in required |
| Service Class 12 | Site is serviceable by copper, jumpering is required |
| Service Class 13 | Site is serviceable by copper, all infrastructure is in place. |
| Service Class 20 | Site will be serviced by cable (HFC). |
| Service Class 21 | The property is within the HFC footprint, no drop, wall plate or NTD |
| Service Class 22 | The property is within the HFC footprint, drop in place, no wall plate or NTD |
| Service Class 23 | The property is within the HFC footprint, drop and wall plate in place, no NTD |
| Service Class 24 | The property is within the HFC footprint, drop, wall plate and NTD in place. |
| Service Class 30 | The property will be serviced by FTTC technology. |
| Service Class 31 | The property is within the FTTC footprint, copper lead in is required. |
| Service Class 32 | The property is within the FTTC footprint. Copper lead in is present but not connected to DPU. An NCD is required. |
| Service Class 33 | The property is within the FTTC footprint. Property is connected to DPU but an NCD is required. |
| Service Class 34 | The property is within the FTTC footprint. It has previously been transferred to nbn® and can transfer to a new provider without an installation appointment. |